从哪里开始
SQL是从哪被要求解析的呢?
//BaseExecutor.java
@Override
public <E> List<E> query(MappedStatement ms, Object parameter, RowBounds rowBounds, ResultHandler resultHandler) throws SQLException {
// <1> 获得 BoundSql 对象
BoundSql boundSql = ms.getBoundSql(parameter);//↓↓↓↓↓
// <2> 创建 CacheKey 对象
CacheKey key = createCacheKey(ms, parameter, rowBounds, boundSql);
return query(ms, parameter, rowBounds, resultHandler, key, boundSql);
}
boundSql长啥样?
/**
*一次可执行的 SQL 封装
*/
public class BoundSql {
/**
* SQL 语句
*/
private final String sql;
/**
* 参数映射列表,SQL 中的每个 #{xxx} 占位符都会被解析成相
* 应的 ParameterMapping 对象
*/
private final List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings;
/**
* 运行时参数,即用户传入的参数,比如 User 对象,或是其他的参数
*/
private final Object parameterObject;
/**
* 附加参数集合,用于存储一些额外的信息,比如 datebaseId
*/
private final Map<String, Object> additionalParameters;
/**
* {@link #additionalParameters} 的 元数据 对象
*/
private final MetaObject metaParameters;
}
解析过程
//MappedStatement.java
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);//↓↓↓↓↓
List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = boundSql.getParameterMappings();
if (parameterMappings == null || parameterMappings.isEmpty()) {
boundSql = new BoundSql(configuration, boundSql.getSql(), parameterMap.getParameterMappings(), parameterObject);
}
for (ParameterMapping pm : boundSql.getParameterMappings()) {
String rmId = pm.getResultMapId();
if (rmId != null) {
ResultMap rm = configuration.getResultMap(rmId);
if (rm != null) {
hasNestedResultMaps |= rm.hasNestedResultMaps();
}
}
}
return boundSql;
}
//DynamicSqlSource.java
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
//DynamicContext存有解析后的sql,主要包含appendSql和getSql方法
DynamicContext context = new DynamicContext(configuration, parameterObject);
//解析SQL片段,并将解析结果存储到DynamicContext中
rootSqlNode.apply(context);//↓↓↓↓↓
SqlSourceBuilder sqlSourceParser = new SqlSourceBuilder(configuration);
Class<?> parameterType = parameterObject == null ? Object.class : parameterObject.getClass();
//构建StaticSqlSource,在此过程中sql语句中的占位符#{}会替换为?
//并为每个占位符构建相应的ParameterMapping
SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings());//↓↓↓↓↓
//调用StaticSqlSource的getBoundSql获取BoundSql
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
//将DynamicContext的ContextMap(上下文的参数集合)中的内容拷贝到BoundSql中
context.getBindings().forEach(boundSql::setAdditionalParameter);
return boundSql;
}
对于一个包含了${}占位符,或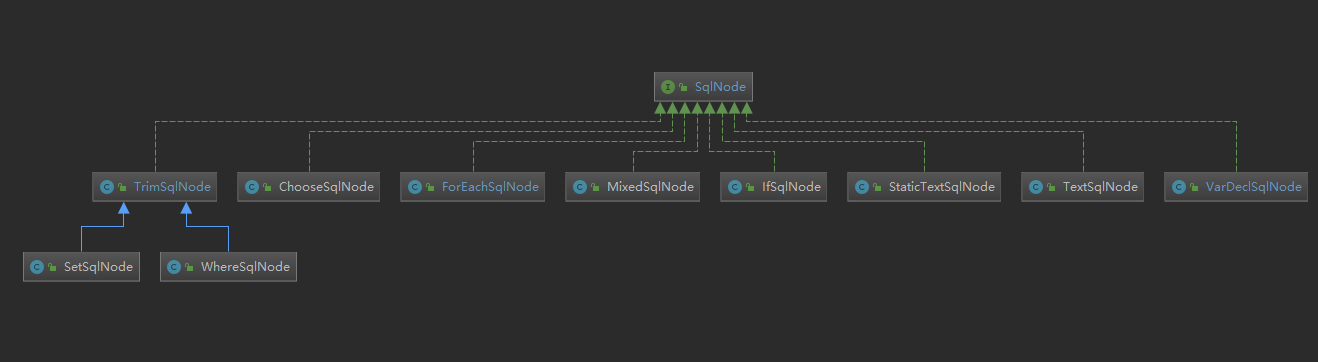
StaticTextSqlNode 用于存储静态文本,TextSqlNode用于存储带有${}占位 符的文本,IfSqlNode 则用于存储
MixedSqlNode
public class MixedSqlNode implements SqlNode {
private final List<SqlNode> contents;
public MixedSqlNode(List<SqlNode> contents) {
this.contents = contents;
}
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
//遍历 然后调用SqlNode对象本身的apply方法解析sql
contents.forEach(node -> node.apply(context));//↓↓↓↓↓
return true;
}
}
MixedSqlNode 可以看做是 SqlNode 实现类对象的容器,凡是实现了 SqlNode 接口的类 都可以存储到 MixedSqlNode 中,包括它自己。MixedSqlNode 解析方法 apply 逻辑比较简单, 即遍历 SqlNode 集合,并调用其他 SalNode 实现类对象的 apply 方法解析 sql。
StaticTextSqlNode
//StaticTextSqlNode 用于存储静态文本,所以它不需要什么解析逻辑
//直接将其存储的SQL 片段添加到 DynamicContext 中即可
public class StaticTextSqlNode implements SqlNode {
private final String text;
public StaticTextSqlNode(String text) {
this.text = text;
}
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
context.appendSql(text);
return true;
}
}
TextSqlNode
public class TextSqlNode implements SqlNode {
private final String text;
private final Pattern injectionFilter;
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
//创建${}占位符解析器
GenericTokenParser parser = createParser(new BindingTokenParser(context, injectionFilter));
//解析${}占位符,并将结果添加到DynamicContext
context.appendSql(parser.parse(text));//↓↓↓↓↓
return true;
}
private GenericTokenParser createParser(TokenHandler handler) {
//创建占位符解析器,GenericTokenParser是一个通用解析器
//并非只能解析${}占位符
return new GenericTokenParser("${", "}", handler);
}
}
/**
* GenericTokenParser 是一个通用的标记解析器,用于解析形如${xxx},#{xxx}等标
记 。
*GenericTokenParser 负责将标记中的内容抽取出来,并将标记内容交给相应的
TokenHandler 去处理。
*/
public class GenericTokenParser {
private final String openToken;
private final String closeToken;
private final TokenHandler handler;
public GenericTokenParser(String openToken, String closeToken, TokenHandler handler) {
this.openToken = openToken;
this.closeToken = closeToken;
this.handler = handler;
}
/**
* 解析以 openToken 开始,以 closeToken 结束的 Token ,并提交给 handler(TokenHandler ) 进行处理
*/
public String parse(String text) {
if (text == null || text.isEmpty()) {
return "";
}
// search open token
// 寻找开始的 openToken 的位置
int start = text.indexOf(openToken);
// 找不到,直接返回
if (start == -1) {
return text;
}
char[] src = text.toCharArray();
// 起始查找位置
int offset = 0;
// 结果
final StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder();
// 匹配到 openToken 和 closeToken 之间的表达式
StringBuilder expression = null;
while (start > -1) {
// 转义字符
if (start > 0 && src[start - 1] == '\\') {
// this open token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
// 因为 openToken 前面一个位置是 \ 转义字符,所以忽略 \
// 添加 [offset, start - offset - 1] 和 openToken 的内容,添加到 builder 中
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset - 1).append(openToken);
// 修改 offset
offset = start + openToken.length();
} else {
// found open token. let's search close token.
if (expression == null) {
// 创建/重置 expression 对象
expression = new StringBuilder();
} else {
expression.setLength(0);
}
builder.append(src, offset, start - offset);
offset = start + openToken.length();
// 寻找结束的 closeToken 的位置
int end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
while (end > -1) {
if (end > offset && src[end - 1] == '\\') {
// this close token is escaped. remove the backslash and continue.
// 因为 endToken 前面一个位置是 \ 转义字符,所以忽略 \
// 添加 [offset, end - offset - 1] 和 endToken 的内容,添加到 builder 中
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset - 1).append(closeToken);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
// 继续,寻找结束的 closeToken 的位置
end = text.indexOf(closeToken, offset);
} else {
expression.append(src, offset, end - offset);
offset = end + closeToken.length();
break;
}
}
// 拼接内容
if (end == -1) {
// closeToken 未找到,直接拼接
builder.append(src, start, src.length - start);
// 修改 offset
offset = src.length;
} else {
// closeToken 找到,将 expression 提交给 handler 处理 ,并将处理结果添加到 builder 中
builder.append(handler.handleToken(expression.toString()));//↓↓↓↓↓
offset = end + closeToken.length();
}
}
// 继续,寻找开始的 openToken 的位置
start = text.indexOf(openToken, offset);
}
// 拼接剩余的部分
if (offset < src.length) {
builder.append(src, offset, src.length - offset);
}
return builder.toString();
}
}
//TextSqlNode内部类
//BindingTokenParser 负责解析标记内容,并将解析结果返回给GenericTokenParser,用于替换${xxx}标记。
private static class BindingTokenParser implements TokenHandler {
private DynamicContext context;
private Pattern injectionFilter;
public BindingTokenParser(DynamicContext context, Pattern injectionFilter) {
this.context = context;
this.injectionFilter = injectionFilter;
}
@Override
public String handleToken(String content) {
Object parameter = context.getBindings().get("_parameter");
if (parameter == null) {
context.getBindings().put("value", null);
} else if (SimpleTypeRegistry.isSimpleType(parameter.getClass())) {
context.getBindings().put("value", parameter);
}
//通过 ONGL 从用户传入的参数中获取结果
Object value = OgnlCache.getValue(content, context.getBindings());
String srtValue = value == null ? "" : String.valueOf(value);
//通过正则表达式检测 srtValue 有效性
checkInjection(srtValue);
return srtValue;
}
private void checkInjection(String value) {
if (injectionFilter != null && !injectionFilter.matcher(value).matches()) {
throw new ScriptingException("Invalid input. Please conform to regex" + injectionFilter.pattern());
}
}
}
IfSqlNode
public class IfSqlNode implements SqlNode {
private final ExpressionEvaluator evaluator;
private final String test;
private final SqlNode contents;
public IfSqlNode(SqlNode contents, String test) {
this.test = test;
this.contents = contents;
this.evaluator = new ExpressionEvaluator();
}
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
//通过 OGNL 评估 test 表达式的结果
//若 test 表达式中的条件成立,则调用其它节点的apply方法进行解析
if (evaluator.evaluateBoolean(test, context.getBindings())) {
//是<if>节点中也可嵌套其他的动态节点,并非只有纯文本。
//因此 contents 变量遍历指向的是 MixedSqlNode,而非 StaticTextSqlNode。
contents.apply(context);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
TrimSqlNode
//TrimSqlNode.java
@Override
public boolean apply(DynamicContext context) {
// 创建具有过滤功能的 DynamicContext
FilteredDynamicContext filteredDynamicContext = new FilteredDynamicContext(context);//↓↓↓↓↓
boolean result = contents.apply(filteredDynamicContext);
//// 过滤掉前缀和后缀
filteredDynamicContext.applyAll();
return result;
}
private class FilteredDynamicContext extends DynamicContext {
private DynamicContext delegate;
private boolean prefixApplied;
private boolean suffixApplied;
private StringBuilder sqlBuffer;
public FilteredDynamicContext(DynamicContext delegate) {
super(configuration, null);
this.delegate = delegate;
this.prefixApplied = false;
this.suffixApplied = false;
this.sqlBuffer = new StringBuilder();
}
public void applyAll() {
sqlBuffer = new StringBuilder(sqlBuffer.toString().trim());
String trimmedUppercaseSql = sqlBuffer.toString().toUpperCase(Locale.ENGLISH);
if (trimmedUppercaseSql.length() > 0) {
// 对 sql 进行过滤操作,移除掉前缀或后缀
applyPrefix(sqlBuffer, trimmedUppercaseSql);
applySuffix(sqlBuffer, trimmedUppercaseSql);
}
// 将当前对象的 sqlBuffer 内容添加到代理类中
delegate.appendSql(sqlBuffer.toString());
}
private void applyPrefix(StringBuilder sql, String trimmedUppercaseSql) {
if (!prefixApplied) {
// 设置 prefixApplied 为 true,以下逻辑仅会被执行一次
prefixApplied = true;
if (prefixesToOverride != null) {
for (String toRemove : prefixesToOverride) {
// 检测当前 sql 字符串是否包含前缀,比如 'AND ', 'AND\t'等
if (trimmedUppercaseSql.startsWith(toRemove)) {
sql.delete(0, toRemove.trim().length());
break;
}
}
}
// 插入前缀,比如 WHERE
if (prefix != null) {
sql.insert(0, " ");
sql.insert(0, prefix);
}
}
}
private void applySuffix(StringBuilder sql, String trimmedUppercaseSql) {
if (!suffixApplied) {
suffixApplied = true;
if (suffixesToOverride != null) {
for (String toRemove : suffixesToOverride) {
if (trimmedUppercaseSql.endsWith(toRemove) || trimmedUppercaseSql.endsWith(toRemove.trim())) {
int start = sql.length() - toRemove.trim().length();
int end = sql.length();
sql.delete(start, end);
break;
}
}
}
if (suffix != null) {
sql.append(" ");
sql.append(suffix);
}
}
}
}
WhereSqlNode
//基于 TrimSqlNode 实现
public class WhereSqlNode extends TrimSqlNode {
private static List<String> prefixList = Arrays.asList("AND ","OR ","AND\n", "OR\n", "AND\r", "OR\r", "AND\t", "OR\t");
public WhereSqlNode(Configuration configuration, SqlNode contents) {
super(configuration, contents, "WHERE", prefixList, null, null);
}
}
SetSqlNode
//同上
public class SetSqlNode extends TrimSqlNode {
private static final List<String> COMMA = Collections.singletonList(",");
public SetSqlNode(Configuration configuration,SqlNode contents) {
super(configuration, contents, "SET", COMMA, null, COMMA);
}
}
经过前面的解析,我们已经能从 DynamicContext 获取到完整的 SQL 语句了。但这并不 意味着解析过程就结束了,因为当前的 SQL 语句中还有一种占位符没有处理,即#{}。与${} 占位符的处理方式不同,MyBatis 并不会直接将#{}占位符替换为相应的参数值。
//构建StaticSqlSource,在此过程中sql语句中的占位符#{}会替换为?
//并为每个占位符构建相应的ParameterMapping
SqlSource sqlSource = sqlSourceParser.parse(context.getSql(), parameterType, context.getBindings());
接着这一句往下分析
//SqlSourceBuilder.java
public SqlSource parse(String originalSql, Class<?> parameterType, Map<String, Object> additionalParameters) {
// 创建 #{} 占位符处理器
ParameterMappingTokenHandler handler = new ParameterMappingTokenHandler(configuration, parameterType, additionalParameters);
// 创建 #{} 占位符解析器
GenericTokenParser parser = new GenericTokenParser("#{", "}", handler);
// 解析 #{} 占位符,并返回解析结果,源码上面分析过了
String sql = parser.parse(originalSql);
// 封装解析结果到 StaticSqlSource 中,并返回
return new StaticSqlSource(configuration, sql, handler.getParameterMappings());
}
GenericTokenParser 负责将#{}占位符中的内容抽取出来,并将抽取出的内容传给 handleToken 方法。handleToken 方法负责将传入的参数解析成对应的 ParameterMapping 对象,这步操作由 ParameterMappingTokenHandler方法完成。
//SqlSourceBuilder内部类
private static class ParameterMappingTokenHandler extends BaseBuilder implements TokenHandler {
private List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings = new ArrayList<>();
private Class<?> parameterType;
private MetaObject metaParameters;
public ParameterMappingTokenHandler(Configuration configuration, Class<?> parameterType, Map<String, Object> additionalParameters) {
super(configuration);
this.parameterType = parameterType;
this.metaParameters = configuration.newMetaObject(additionalParameters);
}
public List<ParameterMapping> getParameterMappings() {
return parameterMappings;
}
@Override
public String handleToken(String content) {
//parameterMappings为SqlSourceBuilder的成员变量,构造返回的StaticSqlSource用
parameterMappings.add(buildParameterMapping(content));
//就直接返回个?
return "?";
}
private ParameterMapping buildParameterMapping(String content) {
Map<String, String> propertiesMap = parseParameterMapping(content);
String property = propertiesMap.get("property");
Class<?> propertyType;
if (metaParameters.hasGetter(property)) {
propertyType = metaParameters.getGetterType(property);
} else if (typeHandlerRegistry.hasTypeHandler(parameterType)) {
propertyType = parameterType;
} else if (JdbcType.CURSOR.name().equals(propertiesMap.get("jdbcType"))) {
propertyType = java.sql.ResultSet.class;
} else if (property == null || Map.class.isAssignableFrom(parameterType)) {
propertyType = Object.class;
} else {
MetaClass metaClass = MetaClass.forClass(parameterType, configuration.getReflectorFactory());
if (metaClass.hasGetter(property)) {
propertyType = metaClass.getGetterType(property);
} else {
propertyType = Object.class;
}
}
ParameterMapping.Builder builder = new ParameterMapping.Builder(configuration, property, propertyType);
Class<?> javaType = propertyType;
String typeHandlerAlias = null;
for (Map.Entry<String, String> entry : propertiesMap.entrySet()) {
String name = entry.getKey();
String value = entry.getValue();
if ("javaType".equals(name)) {
javaType = resolveClass(value);
builder.javaType(javaType);
} else if ("jdbcType".equals(name)) {
builder.jdbcType(resolveJdbcType(value));
} else if ("mode".equals(name)) {
builder.mode(resolveParameterMode(value));
} else if ("numericScale".equals(name)) {
builder.numericScale(Integer.valueOf(value));
} else if ("resultMap".equals(name)) {
builder.resultMapId(value);
} else if ("typeHandler".equals(name)) {
typeHandlerAlias = value;
} else if ("jdbcTypeName".equals(name)) {
builder.jdbcTypeName(value);
} else if ("property".equals(name)) {
// Do Nothing
} else if ("expression".equals(name)) {
throw new BuilderException("Expression based parameters are not supported yet");
} else {
throw new BuilderException("An invalid property '" + name + "' was found in mapping #{" + content + "}. Valid properties are " + PARAMETER_PROPERTIES);
}
}
if (typeHandlerAlias != null) {
builder.typeHandler(resolveTypeHandler(javaType, typeHandlerAlias));
}
return builder.build();
}
private Map<String, String> parseParameterMapping(String content) {
try {
return new ParameterExpression(content);
} catch (BuilderException ex) {
throw ex;
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new BuilderException("Parsing error was found in mapping #{" + content + "}. Check syntax #{property|(expression), var1=value1, var2=value2, ...} ", ex);
}
}
}
接着主线往下走,别岔咯
//调用StaticSqlSource的getBoundSql获取BoundSql
BoundSql boundSql = sqlSource.getBoundSql(parameterObject);
public class StaticSqlSource implements SqlSource {
private final String sql;
private final List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings;
private final Configuration configuration;
public StaticSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql) {
this(configuration, sql, null);
}
public StaticSqlSource(Configuration configuration, String sql, List<ParameterMapping> parameterMappings) {
this.sql = sql;
this.parameterMappings = parameterMappings;
this.configuration = configuration;
}
@Override
public BoundSql getBoundSql(Object parameterObject) {
return new BoundSql(configuration, sql, parameterMappings, parameterObject);
}
}
很简单,没什么好说的
然后就没有然后了
至此SQL解析完毕



